Mapping of Availability Zones and Host-Aggregates to vSphere Clusters
In an OpenStack environment, the communication between the compute API/scheduling layer (NOVA) and the hypervisor is done by the Nova-Compute process, also called a Nova-Compute node:
In vSphere environments, this Nova-Compute process is decoupled from the VMware vSphere Server. The Nova-Compute process uses the VMware vCenter API to control groups of vSphere ESXi servers through vCenter Server. In VMware Integrated OpenStack, the Nova-Compute process runs on a separate VM called the ComputeDriver VM.
Figure 11. Nova Components Overview
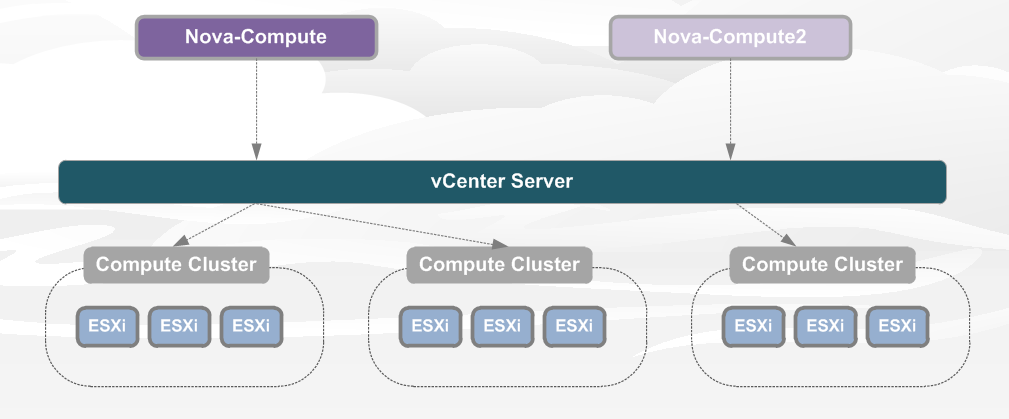
There is a 1:1 relationship between the Nova-Compute process (ComputeDriver VM) and a vCenter vSphere ESXi cluster. That is, a complete vCenter cluster with all the vSphere ESXi servers is seen as one resource pool by the OpenStack Nova scheduler.
The placement of instances (VMs) can be influenced by the use of availability zones and host aggregates, both of which are a grouping of Nova-Compute nodes.
Availability zones, as the name suggests, is a grouping of Nova-Compute nodes that form a failure domain and are addressed by the user when booting an instance using the “availability-zone” option.
Host aggregates provide a way to further segment an availability zone and group Nova-Compute nodes within an availability zone based on arbitrary characteristics such as hardware types, and are addressed by using extra keys in the OpenStack flavor specification, or by using Image extra properties.
For host aggregates to be taken into account by the Nova Scheduler, a number of non-default extra filter configurations need to be configured in the Nova configuration file of the OpenStack controller. As this extra configuration is not exposed by the current version of VMware Integrated OpenStack, using the host aggregate functionality is not recommended. It is expected that this functionality will be exposed in a future version of VMware Integrated OpenStack.
Due to this, we will only use availability zones in this design to control the placement of instances (VMs).
Design Decisions regarding Availability Zones in VMware Integrated OpenStack
Due to requirements provided by the <Customer>, the following VMware Integrated OpenStack design decisions have also been made.
Table 74. Availability Zone Design Decisions
| Decision ID | Design Decision | Design Justification | Design Implication |
|---|---|---|---|
| For this design, <Customer> has made the following decisions listed in this table. | |||
| Only availability zones will be used to control the placement of instances (VMs). | The current VMware Integrated OpenStack 2.x implementation does not allow the UI configuration of the extra scheduler filters needed for host aggregates. | The placement of instances (VMs) can only be influenced by the higher layers of orchestration (IaaS deployment tools), and not by keys in flavors or images. |